Main Content
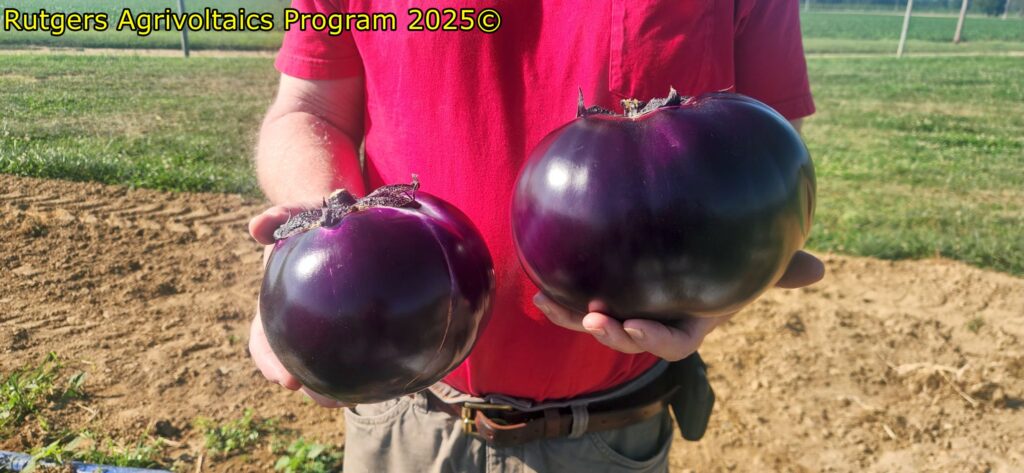

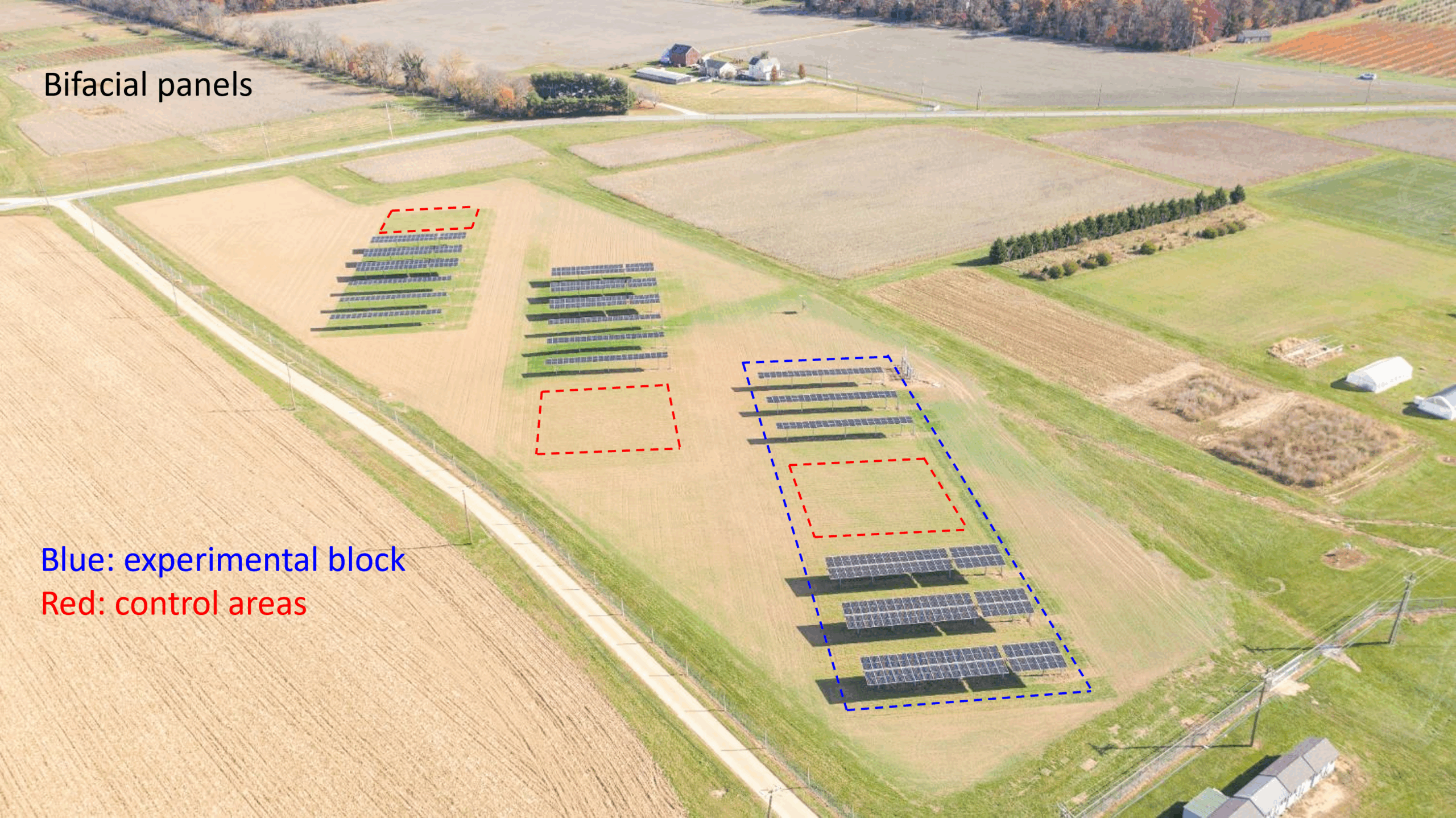
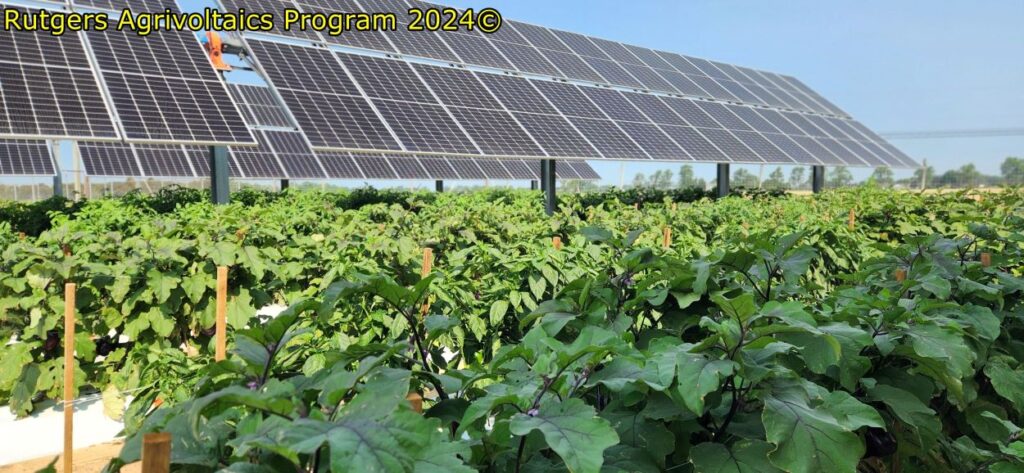
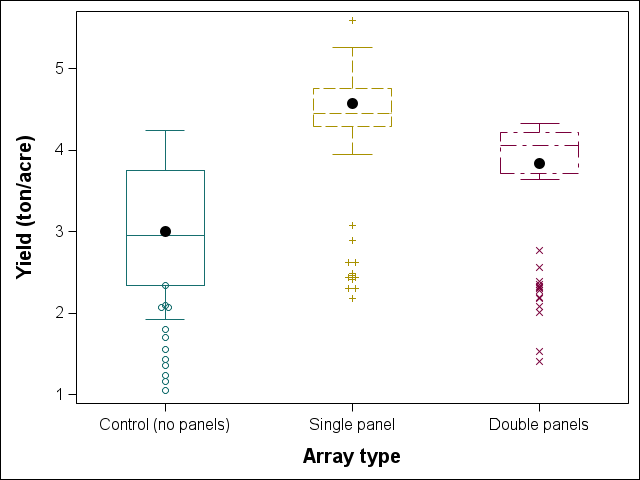
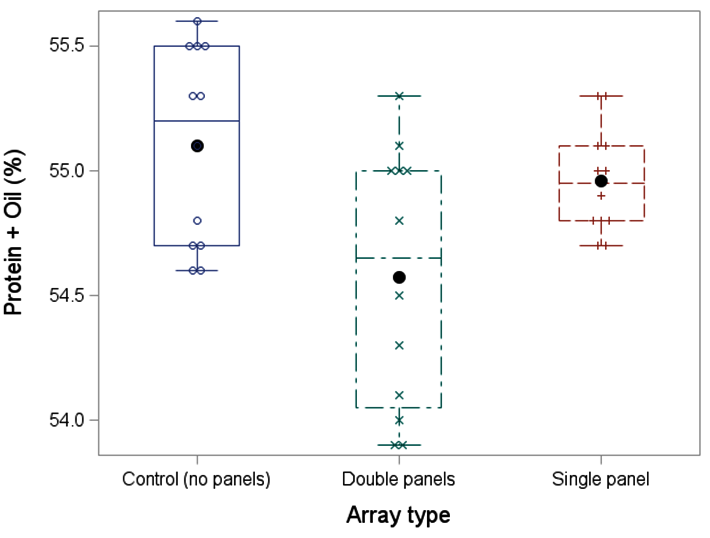
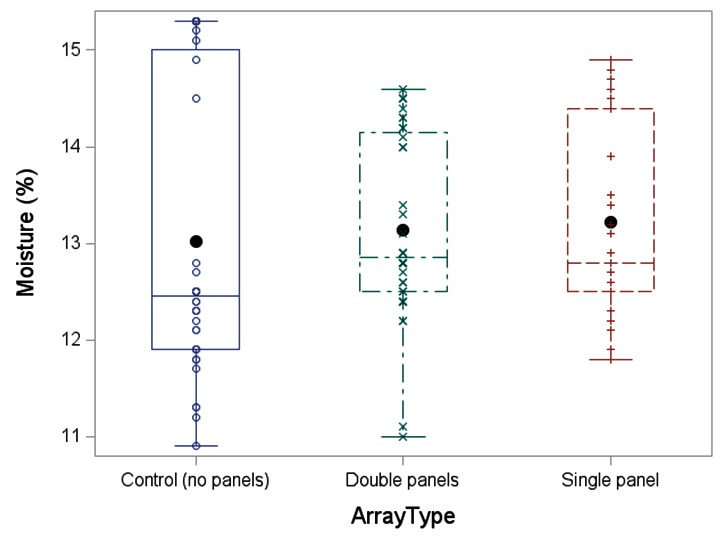
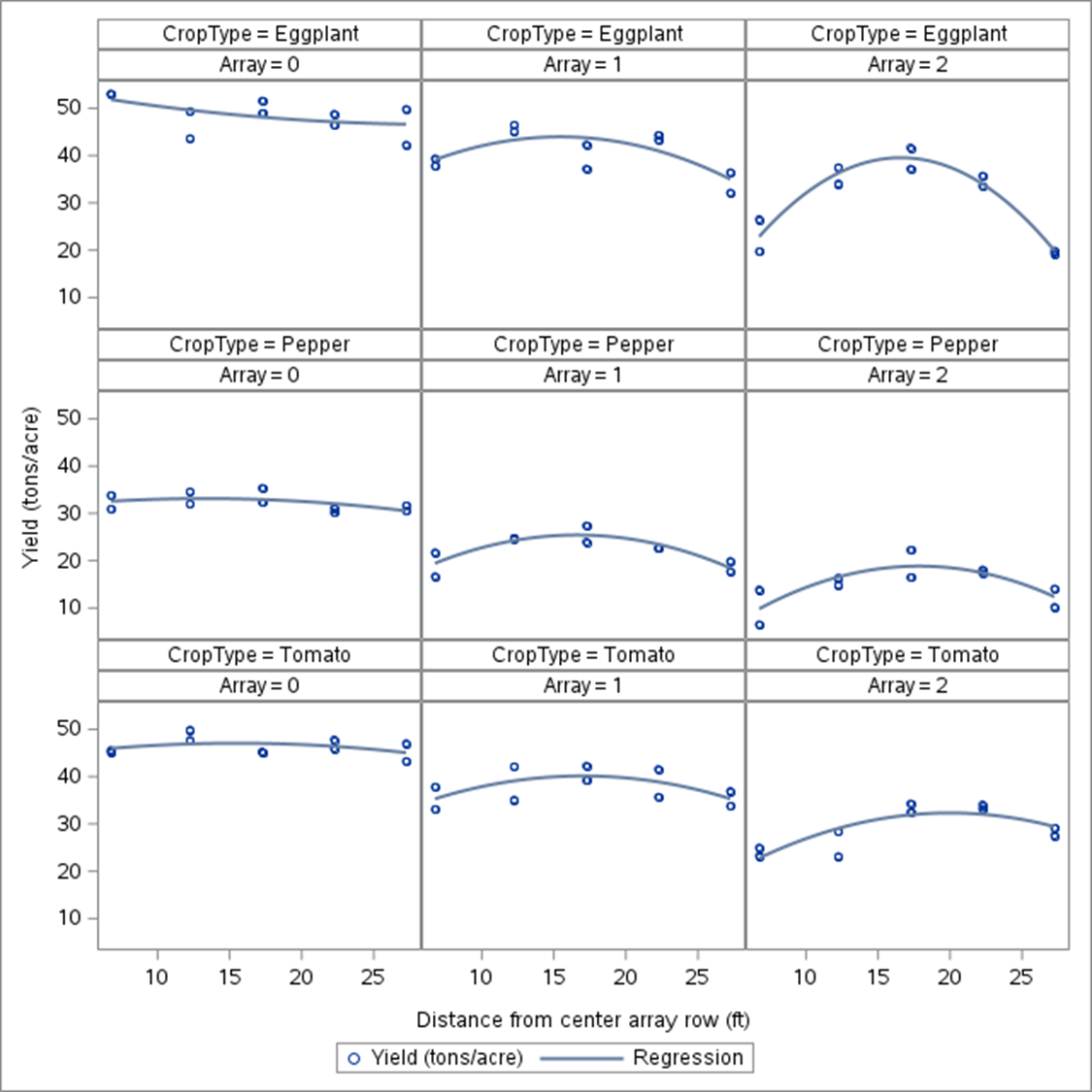
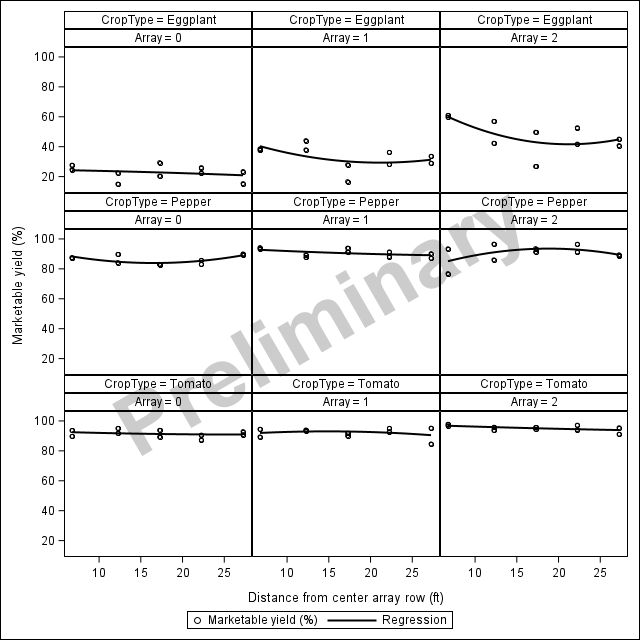
The second year of the specialty crops research at RAREC is moving along! Like last year, fresh-market tomato, silician eggplant, and bell peppers are being grown under no panel (control), single agrivoltaic (AV) panels, and double AV panels in southern New Jersey. This year, specialty crop transplanting was done on 11 June 2025 and to date there has been 9 sicilian eggplant ‘Palermo’, 4 bell pepper ‘Turnpike’, and 2 fresh-market tomato ‘Red Deuce’ harvests with all harvested crops being donated directly to local food banks and churches in southern New Jersey with help the Master Gardener Program of Cumberland County, New Jersey.

Harvesting will continue over the next 5 or 6 weeks with data to be shared at upcoming Extension meetings this winter! Along with the specialty crops research, soybeans have also been planted in two of the agrivoltaics research blocks at RAREC this year!

On September 21, 2025 there will be an event at RAREC near Bridgeton and at the Animal Farm on the campus of Rutgers University celebrating Sun Day! Both events are FREE and will run from 10 AM until noon! Registration is required. For more information on Sun Day please click here.