Main Content
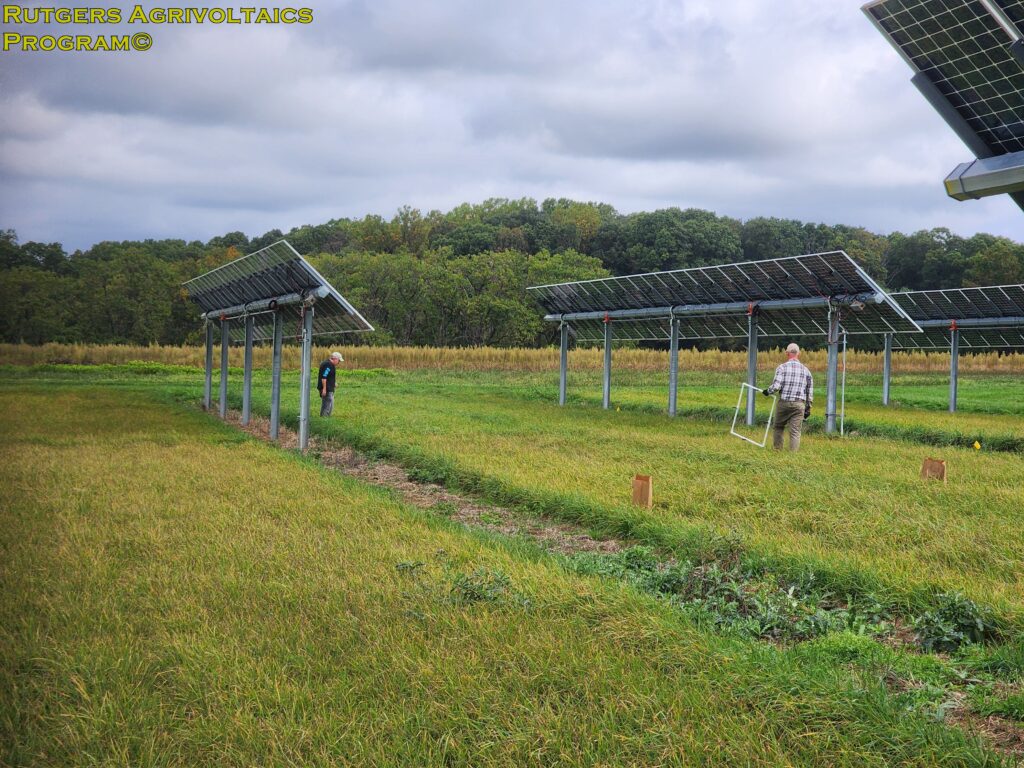
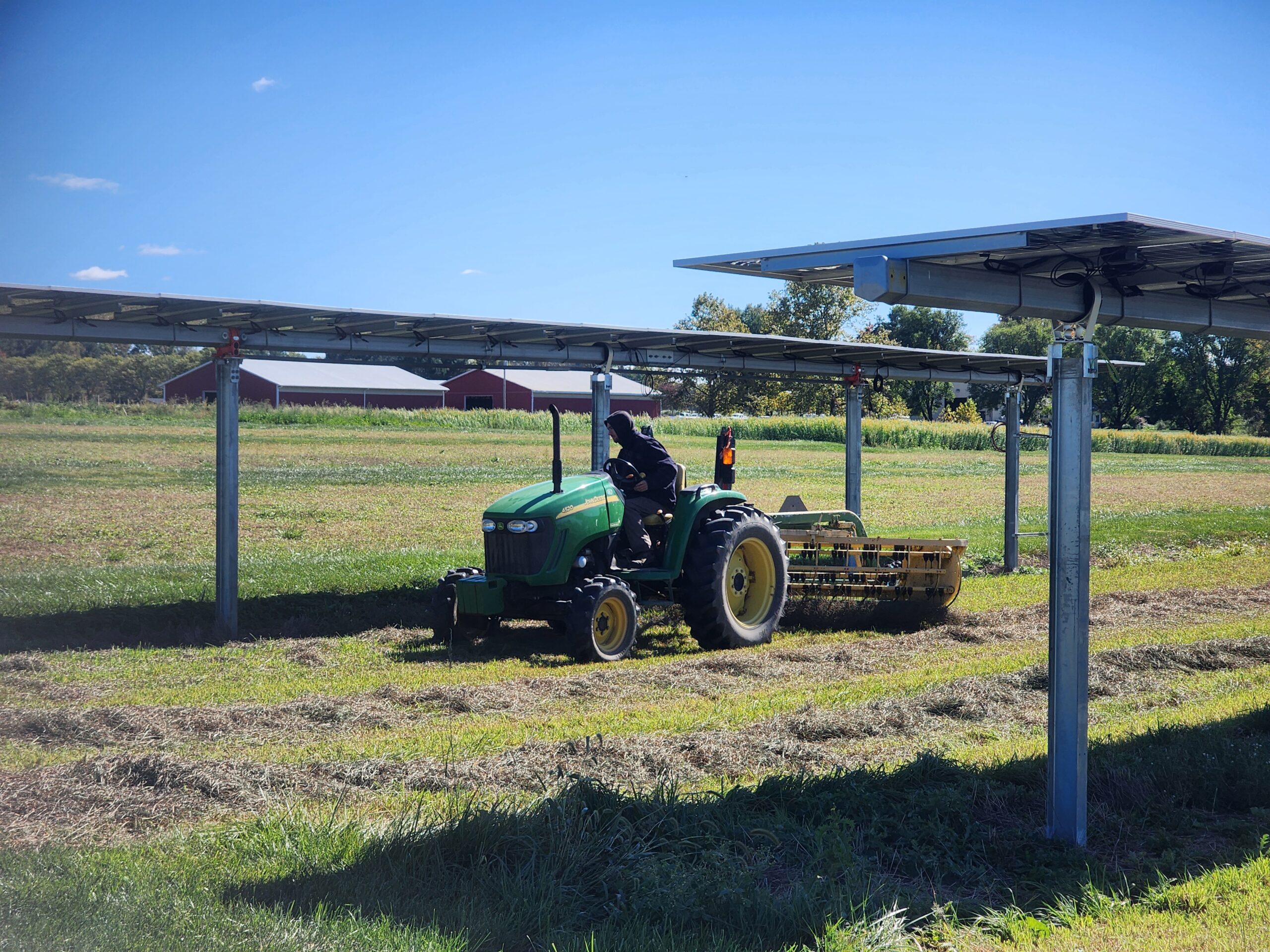
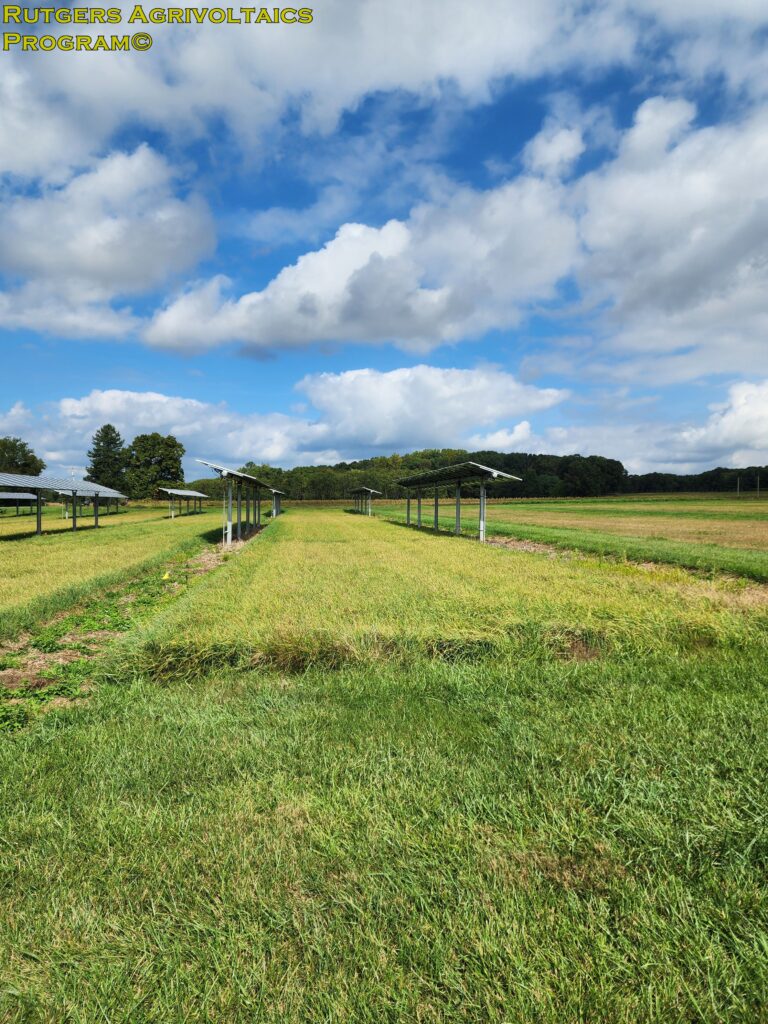
On 3 Oct., Biomass Assessment was conducted at the Snyder Farm for the last time this season. Samples from each sub-plot were collected and fresh weight and dry weight were recorded. On 7 Oct., the third cut was done and the hay allowed to dry down. Moisture measurements were recorded in the windrows and samples sent for quality analysis at the Dairy One’s Forage Laboratory (Ithaca NY) prior to bailing on 10 Oct. This data will be used to determine what effects, if any, the solar arrays had on hay yield and quality.
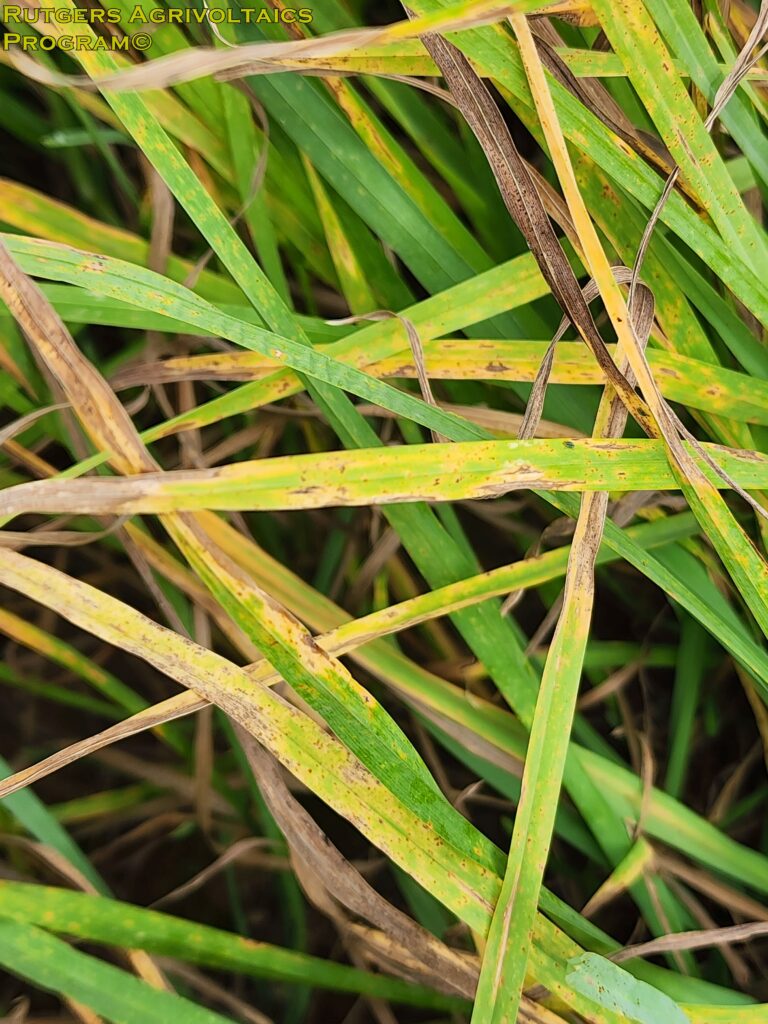
Interestingly, stem rust appeared before the 3rd cutting, starting in the control areas before spreading to the experimental AV areas. More work is needed to determine the impact, if any, of the solar panel arrays on stem rust, and many other common foliar diseases in hay production.
Hay Biomass Sampling
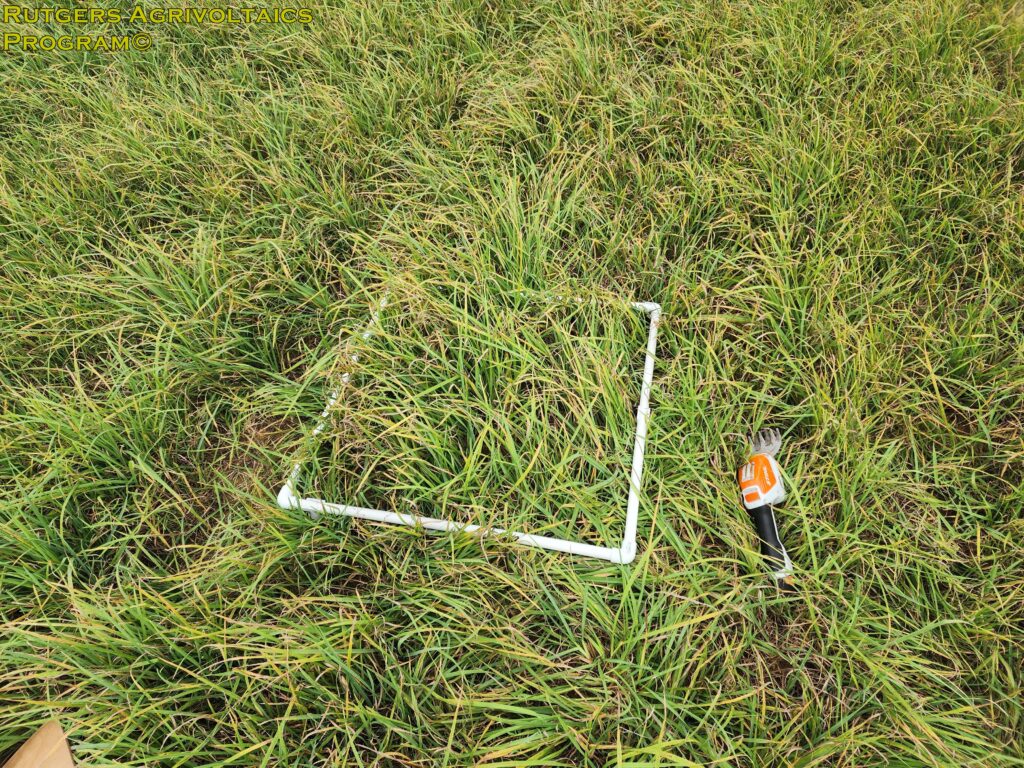

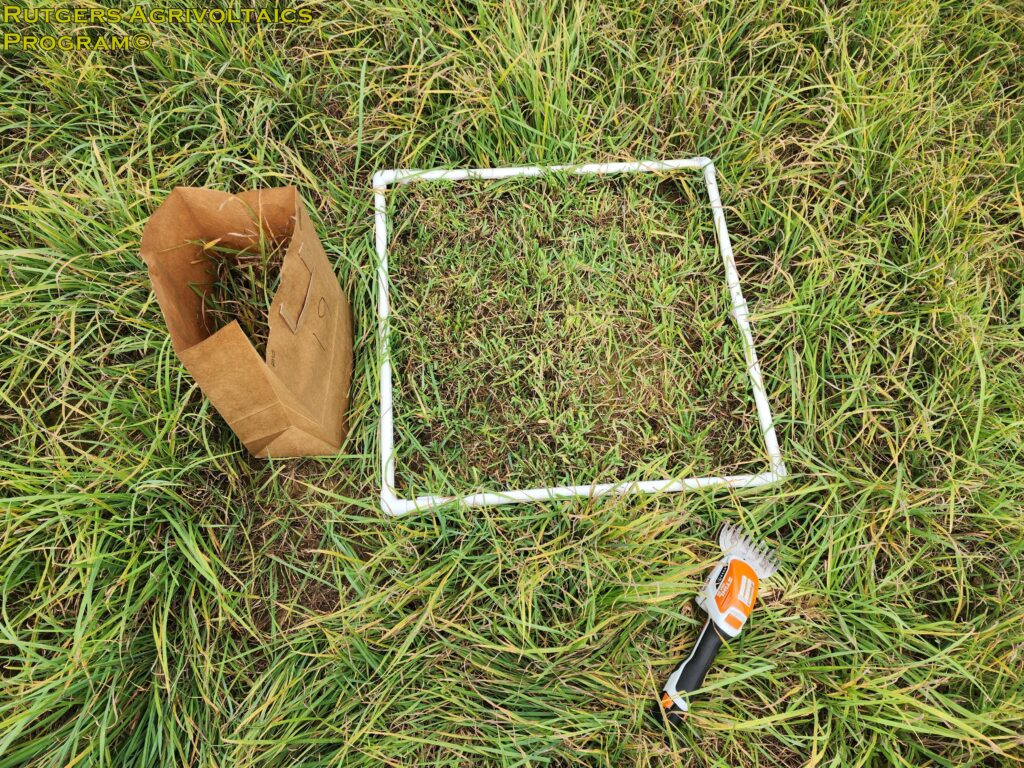
Samples were collected from 24 sub-plots in the two research blocks. Half from control areas not impacted by the solar panel arrays, and half from the experimental areas between the solar panel arrays. Half-meter squares were randomly placed in the sub-plots (left picture). The trimmed hay from each sample collection area were placed into a paper bags that were numbered to identify their location in the field (middle picture). Fresh weight of each sample was measured. The samples were then dried in an industrial oven for >48 hours and dry weight measured.
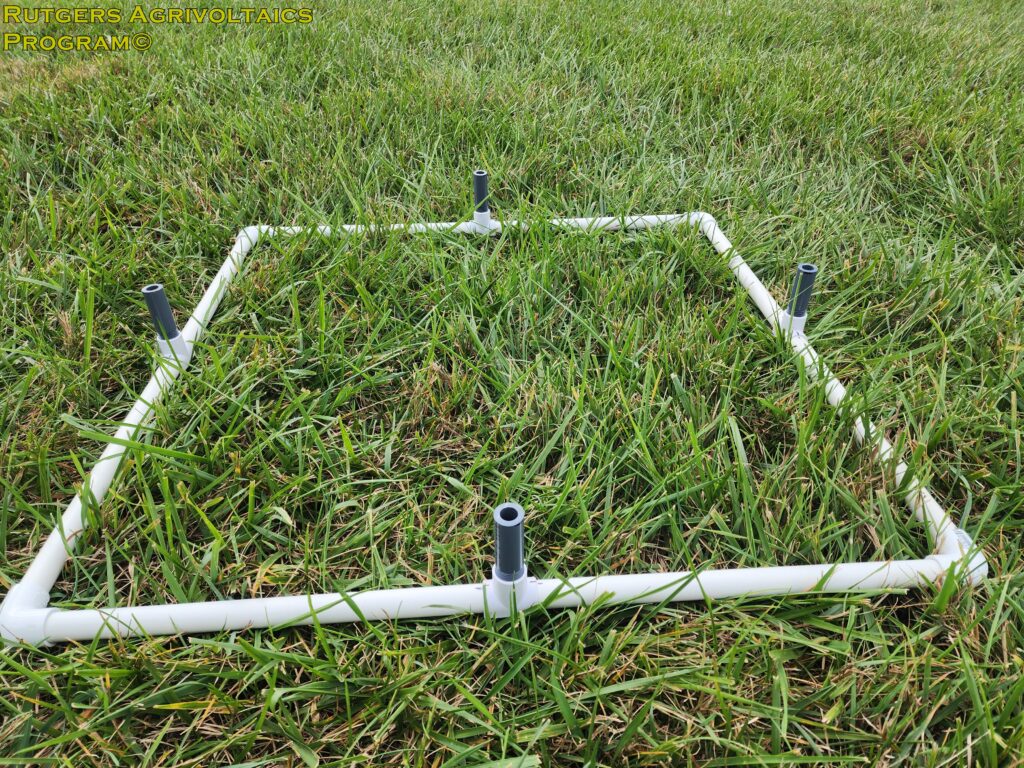
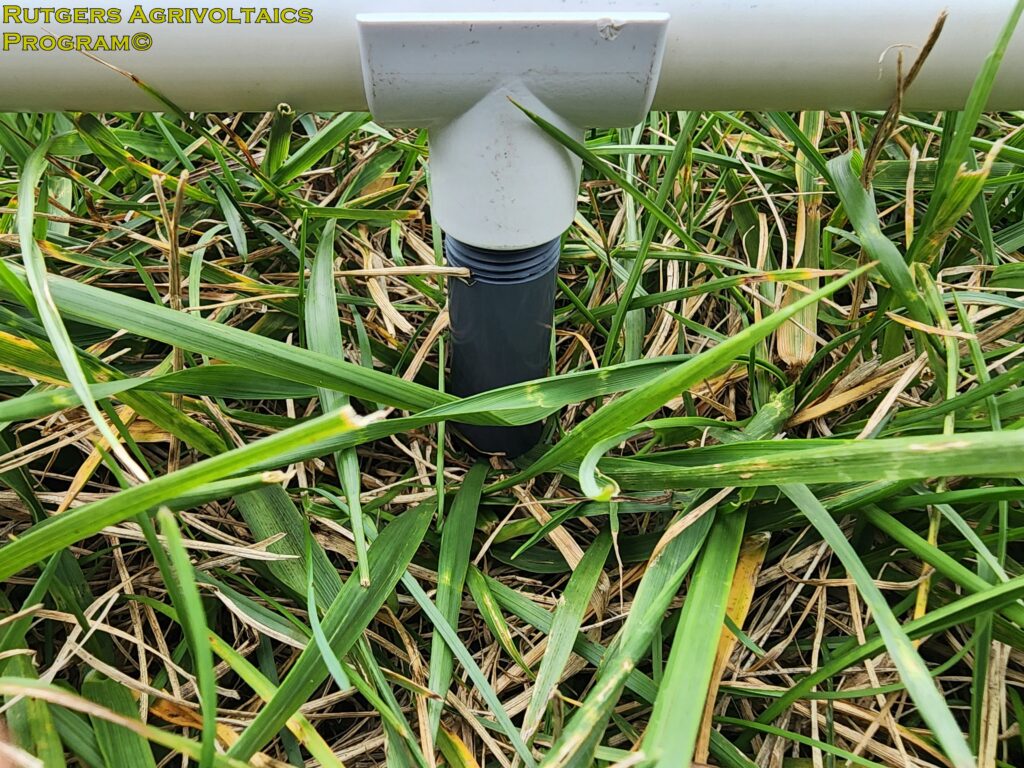
Four-inch PVC legs were used to raise the squares and guide the sample collection process by maintaining a uniform trim height above ground level. This allows for consistent sampling at each location and prevents cutting the hay too short.
Cutting / Moisture Measurements / Quality Analysis
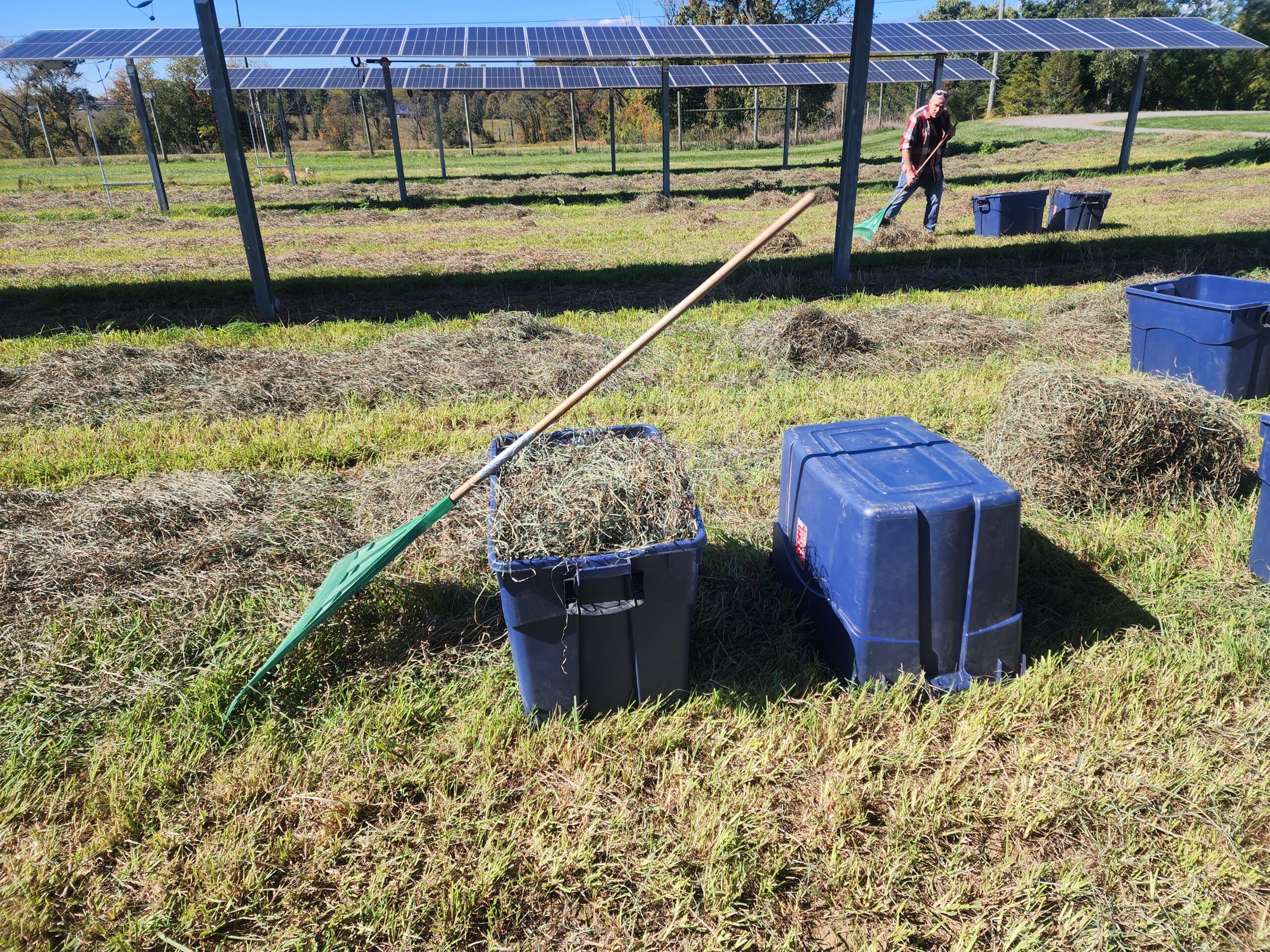

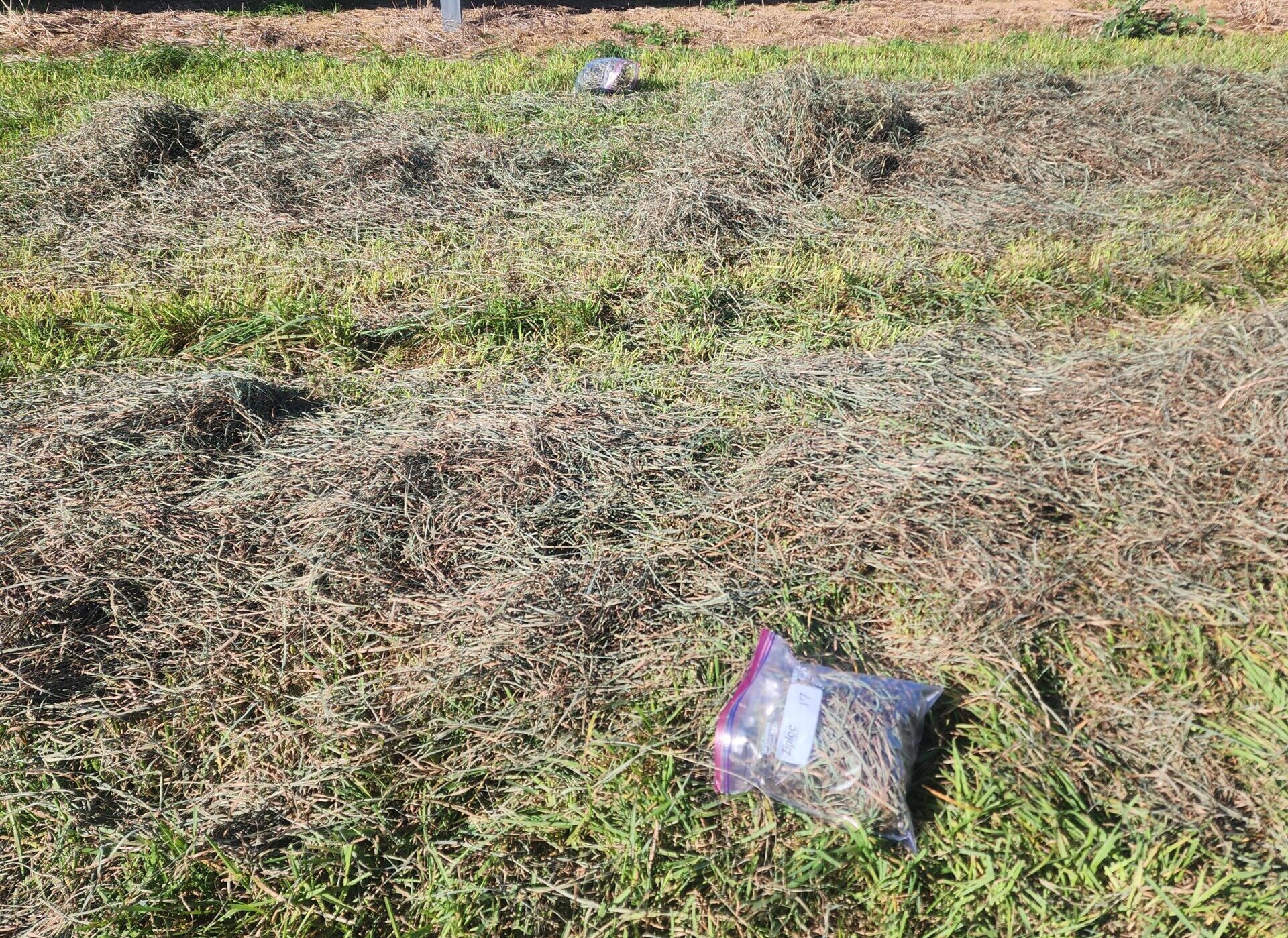
The hay was cut in a manner that left three windrows between the solar arrays and the control area. After a few days, a moisture meter is used to ensure the hay was sufficiently dry for bailing. Twenty-five foot sections of each sub-plot were gathered into bins and weighed (left). A small sample from each sub-plot was bagged and sent for quality analysis (center). Lastly, the hay was bailed and donated to local farms (right).
Stem rust
Stem Rust, Puccinia graminis, was identified on samples sent to the Rutgers Plant Diagnostic Laboratory. The disease first started in the control area, then spread to the experimental area between the solar arrays.
Discover more from Rutgers Agrivoltaics Program
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.






